Electricity
Static Electricity
- How Static Electricity is Produced
- When two different objects that are insulators (such as a plastic rod and silk cloth) are rubbed together, electrons move from one object to another.
- One object becomes negatively-charged, and the other object becomes positively-charged.
- The more rubbing, the more electrons are transferred, and the larger is the charge built up.
- Unlike charges (positive and negative) attract each other.
- Examples of Static Electricity include lightning and the Van de Graaff Generator.
Current Electricity
- Current Electricity or electric current is the movement of negatively-charged electrons through wires or objects with metals, carbon or water.
- Conductors are substances that allow electrons to travel easily through them (e.g. metals, carbon and water).
- Insulators or non-conductors are substances that do not allow electrons to travel easily through them (e.g. plastic and wood).
- Resistors are substances that are poor conductors. They convert much of the energy of moving electrons into light, heat or sound energy in light bulbs and stereos.
The Simple Cell

- A simple cell consists of 2 different conductors (electrodes) partly covered by an acidic or ionic solution (electrolyte solution).
- Different combinations of electrodes produce different voltages. For example, electrodes of zinc and copper produce 1.1 volts, whereas electrodes of aluminium and carbon produce 2.4 volts.
- Rechargeable Cells (e.g. lead-acid cells) are cells that can be recharged when they go 'flat' by reversing the chemical reaction.
- Battery - A battery is a series of connected simple cells.
Common Circuit Diagram Symbols

Series Circuits
- Series Circuit - a circuit where the components are connected one after the other into a 'circle'.
- Ammeter - This device is used to measure current in amperes (A). It must be wired into the circuit in series.
- Disadvantages of Series Circuits - As more light bulbs are connected in series, the brightness of all bulbs decreases.
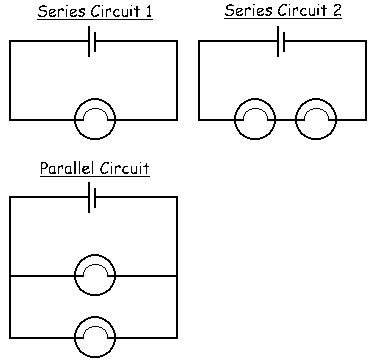
Parallel Circuits
- Parallel Circuits are combined circuits where components such as light bulbs glow equally brightly. This form of wiring is used in household circuits.
- Voltmeter - a device for measuring voltage (or potential difference), and must be wired into the circuit in parallel
- Short Circuit - A short circuit occurs when a conducting object such as a screwdriver lies between two circuits. The electrons take the 'shorter' circuit through the screwdriver.
Household Circuits
- Fuse - The fuse is a thin wire with a low melting point near the power source to a house. It heats up readily and melts to disconnect the circuit to the house when excessive current flows. The fuse may 'blow' in the event of a power surge to the house, or due to a faulty electrical appliance in the house. A circuit-breaker serves a similar purpose.
- Earth Wire - All households must have a connection between the household wiring and the earth. This is to carry away any extra surge of electricity that may occur during lightning storms or as a result of a faulty appliance.
- Electric Plug - Most electric plugs have 3 connections - Active or 'Live' (brown), Neutral (blue) and Earth (green/yellow). However, appliances with plastic exteriors do not always have the third earth connection.
- DC (Direct Current) - Direct current is a current in which electrons continually flow in the one direction. It is produced by batteries.
- AC (Alternating Current) - Alternating current is a current of electrons in which the direction of movement of electrons is continually changing. It is the type of current in household and industrial circuits.
Electricity Generation
- 3 Ways of Generating Electricity
- Using Chemical Reactions in Electric Cells - The chemical energy of the electric cell is converted to electrical energy.
- Using Light in Solar Cells - Solar or photovoltaic cells are made of elements such as silicon which readily free electrons when exposed to sunlight energy. The light energy is converted into electrical energy.
- Using Magnets - Moving a magnet through a coil of wire causes the electrons to flow through the wire. This is called the electromagnetic effect or induction. Moving the magnet in the opposite direction causes the current to reverse. To increase the current, one can increase the strength of the magnet, the number of turns in the coil, or the speed of movement of the magnet.
- Electricity Generation in Coal-Powered Power Stations
Coal is burnt to make heat
![]()
Heat changes water to steam
![]()
Steam turns a propeller-like turbine
![]()
Turbine moves a large magnet back and forth inside a large coil of wire
![]()
A current of electrons is induced in the coil of wire
- Electricity Generation in Hydro-electric Power Stations
Water is stored in a dam at the top of a mountain river
![]()
Water is released from the dam and flows downhill to turn a turbine
![]()
Turbine moves a large magnet back and forth inside a large coil of wire
![]()
A current of electrons is induced in the coil of wire
- Step-up and Step-Down Transformers
A transformer consists of two coils of wire, the primary and the secondary, mounted on the same iron core. Alternating current passing through the primary coil induces a current in the secondary coil.
A step-up transformer is one with a smaller number of turns in the primary coil and a large number of turns in the secondary coil. This increases the current, and is used to boost mains electricity supply over the long distances from the power station to our homes.
A step-down transformer has more turns in the primary coil than the secondary coil. Current is induced in the secondary coil, but the voltage is decreased. This occurs when the 240 volts used in our homes is connected to a child's appliance such as an electric piano or a game.
Ohm's Law

- Voltage or Potential Difference (volts, V) = Current (amperes, A) × Resistance (ohms, Ω)
| I = | V |
| R |
V = I × R
| R = | V |
| I |
Electrical Power
- Electrical power is the amount of electrical energy used by an appliance every second. It is measured in Watts.
- When paying for electricity, we use the unit kiloWatt-hour (kWh). One kWh is the energy used by a 1000 watt appliance switched on for one hour.
- Example:
Q. A 200 watt TV set is used for 6 hours. How many kilowatt-hours of electricity were used?
| A. Number of kWh | = kilowatts × number of rating hours |
| = (200 W⁄1000) × 6 h | |
| = 1.2 kWh |